News
18.08.2020
Today, thirteen employees of our laboratory have received the “CNC Machine Operator” certificates after completing the 144-hour training course at Dubna State University. We congratulate all of them for reaching a new stage in their professional development! Good luck and new accomplishments!
13.08.2020
The winners of the 2019 DLNP Research Award Competition have been announced:
• In the category “Physics”, the winner is the research group, including A. V. Vishneva, M. B. Gromov, O. Yu. Smirnov, for the “Neutrino geophysics” paper series.
• In the category “Methodological and Applied Research”, the winner is the research group, including D. V. Ponomarev, S. V. Rozov, D. V. Filosofov, V. V. Timkin, E. A. Yakushev, for the “Novel method of the neutron low flux measurement using iodine-containing scintillators” paper series.
According to the additional voting, the Incentive Prize was awarded for the research “Beam energy measurement on the LINAK-200 accelerator and energy calibration of scintillator detectors by electrons in the energy range from 1 MeV to 25 MeV”. The authors are El-Sayed Abdel-Shakur, M. A. Demichev, M. I. Gostkin, V. V. Kobets, V. G. Kruchonok, A. A. Nozdrin, S. Yu. Porokhovoi.
We heartily congratulate the winners and wish them further scientific attainments and new heights of success!
The DLNP Research Award Competition was initiated to stimulate the scientific activity of DLNP employees, to improve the quality of papers and to support the implementation of the DLNP Topical Plan.
04.08.2020
Samoil Bilenky. Photo by I. Lapenko
On 28 July 2020, the interview with Professor Samoil Mihelevich Bilenky was published on the website "Troitsky Variant - Nauka" (trv-science.ru). The interview was conducted by the journalist Jan Machonin.
How neutrino studies will help physicists reach beyond the Standard Model? Why did scientists not believe at first that neutrinos have mass? How did Bruno Pontecorvo get the idea of neutrino oscillations? How was the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research established and how did it develop? Professor Samoil Mihelevich Bilenky, an adviser to the Directorate of the Laboratory of Theoretical Physics at JINR, talks about these topics. He celebrated his 92nd birthday this year and is still full of energy and remarkable intelligence.
04.08.2020
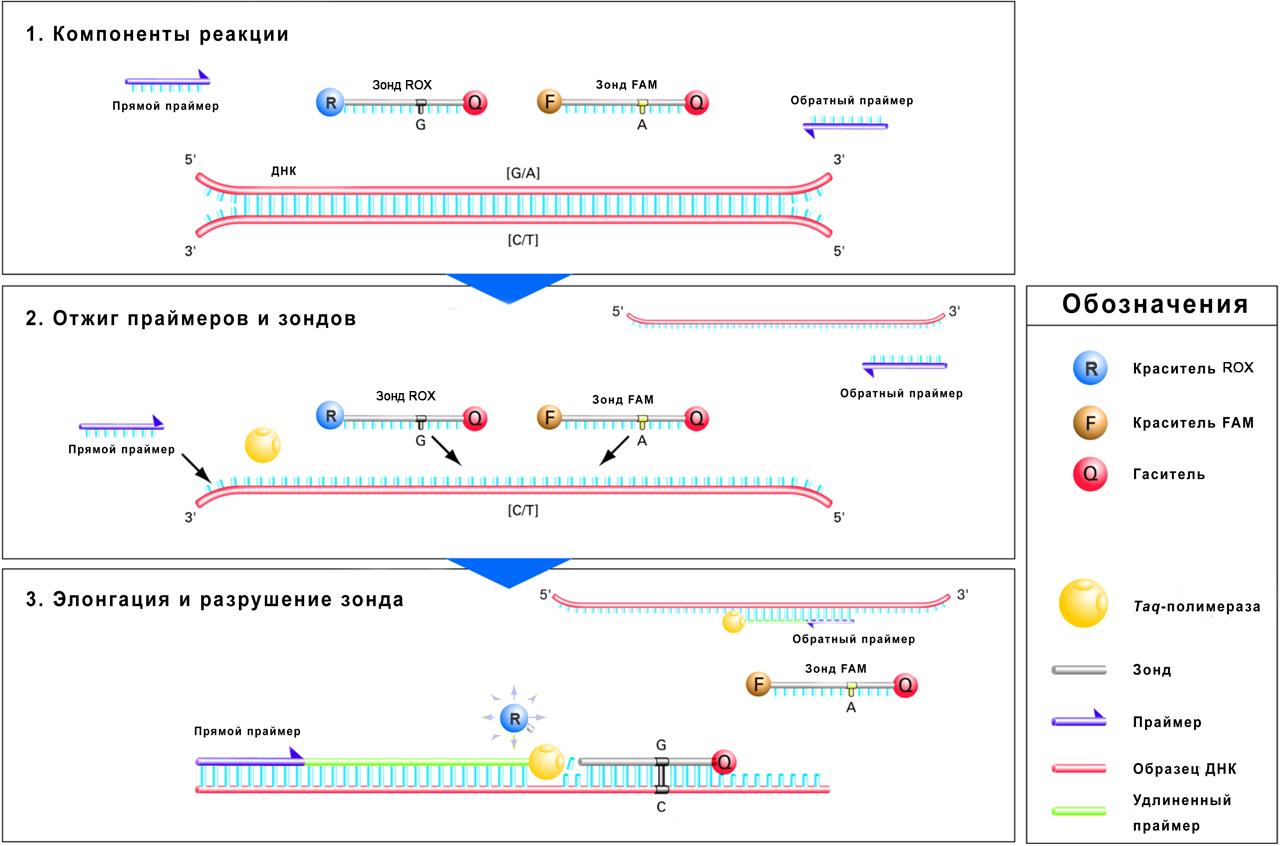
Figure 1. The process of the TaqMan® assay. (https://www.thermofisher.com/ru/ru/home/life-science/pcr/real-time-pcr/real-time-pcr-learning-center/real-time-pcr-basics/how-taqman-assays-work.html with authors’ modifications)
In the present-day world, the study of genetic information becomes more and more important, which generated a novel approach to diagnostics and treatment of different diseases in personalized medicine. The advancements in technology such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and DNA microarrays enabled reducing genome information deciphering time. Nevertheless, their application to routine lab diagnostics seems to be unlikely because of inevitable great investments in equipment and consumables, as well as a considerable amount of time, high risk of sample contamination and deep expertise of researchers. These limitations can be avoided when using the TaqMan method. Its characteristics allow elaborating accurate and low-cost systems for individual risk prediction of diseases related to different single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The systems of this kind do not require either specialized knowledge to perform reactions or expensive equipment and consumables, and their results do not need any additional processing.
23.07.2020
The first prototype magnetic shield for photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) of the OSIRIS facility in the JUNO experiment has arrived at DLNP.
Even a weak magnetic field impairs characteristics of large PMTs, and that is why their perfect functioning can be ensured only by their shielding from the Earth’s magnetic field. To this end, magnetic shields (MSs) for the above project were designed at DLNP.
State-of-the-art material with ultra-high magnetic permeability, so-called metallic glass, an amorphous iron, can be regarded as a special feature of these MSs. The metallic glass production process involves quick heat removal in order to prevent the formation of crystal structure elements, which ensures magnetic permeability 100 times higher than in “standard” permalloy (permalloy is a nickel-iron alloy with soft magnetic properties). It means that we need 100 times less material to create the shielding equivalent to that from permalloy.
22.07.2020
The problem of sterile neutrinos is not extraordinary for physics. There was a time when the solar neutrino deficiency was explained through the existence of these particles. However, their possible detection in nuclear reactor experiments is a quite fresh idea. The team of the Experimental Department of Nuclear Spectroscopy and Radiochemistry at DLNP, JINR, is the leader in the research of this kind.
Studying the physical neutrino processes in an operating power nuclear reactor is not only of scientific but also of absolutely practical value. Neutrinos with their great penetrating ability enable the direct observation of the “heart” of the reactor. And a more comprehensive understanding of the processes inside the reactor can help to increase nuclear fuel efficiency using a spatial pattern of its burning. For this reason, of great importance are calculation and experimental measurement of spectral characteristics of decay products, and, particularly, determination of the energy spectrum of emitted neutrinos.
18.07.2020
Nominees for the DLNP Research Award in the category “Physics”:
1. “Muon capture studies for the matrix elements in ββ decay”.
The JINR authors: D. R. Zinatulina, V. B. Brudanin, V. G. Egorov, M. V. Shirchenko.
2. “First measurement of a long-lived pi+ pi- atom lifetime”.
L. G. Afanasyev, K. I. Gritsai, A. V. Kulikov, L. L. Nemenov, M. V. Nikitin.
17.07.2020
Baikal Neutrino Telescope construction. Photo by B. Shaybonov (JINR)
On 14 July 2020, the interview with Doctor of Physics and Mathematics, Deputy Director for Science of DLNP Dmitry Naumov was published on the website “Troitsky Variant – Nauka”. The interview was performed by the journalist Jan Machonin (Czech Republic). "Troitsky Variant -- Nauka" on 14.07.2020.
Why do neutrinos scarcely interact with ordinary matter, but do pierce through billions of stars? Can neutrinos be representatives of mysterious dark matter? What information about the evolution of galaxies and the Universe do they provide us with? What kind of benefits from the neutrino research are there for “national economy”? Will detectors help to control nuclear weapon production? When will the largest neutrino observatory in the Northern Hemisphere, located at Lake Baikal, be completed? And how to catch neutrinos produced in the Earth’s interior?
The journalist Jan Machonin talked about these topics and many more with Doctor of Physics and Mathematics Dmitry Naumov, a Deputy Director for Science of the Dzhelepov Laboratory of Nuclear Problems at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna.
In his interview he spoke not only about neutrino physics but also about his career, how the Institute managed to survive in the 1990s and how it is functioning now.
07.07.2020
We are delighted to announce that the Dzhelepov Laboratory of Nuclear Problems has subscribed to Overleaf's Group Professional licenses. Overleaf’s premium accounts will enable our researchers to collaborate with internal and external institutions on a wide variety of documents, easily synchronize with Dropbox & GitHub, all whilst keeping their documents and versions well organized.
“Over the last several years, the JINR researchers frequently used Overleaf under individual licenses and were greatly impressed by the tool. From now on, they are enjoying the professional Overleaf licenses significantly boosting their collaboration opportunities.”
Dmitry Naumov Doctor of Physics and Mathematics Deputy Director for Science of DLNP, JINR
06.07.2020
From 2 to 5 June 2020, the online-meeting of the Baikal collaboration (BAIKAL-GVD project) took place. At a time of unprecedented circumstances caused by the COVID-19 outbreak, the meeting was held using the Zoom system. Within three days, 35 reports were made by attendees addressing the results of the expedition 2020, infrastructure development, topics on the GVD-21 deployment, the status of numerical modelling and much more. The Collaboration Committee assembled on 5 June.
04.07.2020
Today, the eldest researcher of the Dzhelepov Laboratory of Nuclear Problems Yulian Aramovich Budagov is 88! Two flipped eights—a double infinity sign—is a rare symbol. Chinese people believed that an eight is a symbol of luck, Jews respected it as God’s number, ancient Greeks found stability and harmony in it, Indians considered it as a fusion of male and female principles in nature. This sign can also be defined as eternity of cognition and everlasting human striving for self-perfection and understanding of the world. We wish Yulian Aramovich not to stop moving towards cognition and harmony in his inside and outside world! Stay strong, active and healthy following this way! May grateful trainees and caring colleagues always surround you! May the Universe give you good chances every day to realize your intentions! And good luck in all you do!
01.07.2020
Can the years spent in ideal conditions eliminate natural selection that affected living organisms for millions of years? It is believed that Homo sapiens is there for about 1600—1800 generations. And with a 25-year-long human generation, it would take hundreds and thousands of years to answer this question. However, using model organisms with a short life cycle but with the life and adaptation processes common for different organisms can give some answers.
Drosophila melanogaster, a fruit fly, is widely used as a model object for studying the way living organisms adapt to environmental changes and inherit certain traits.