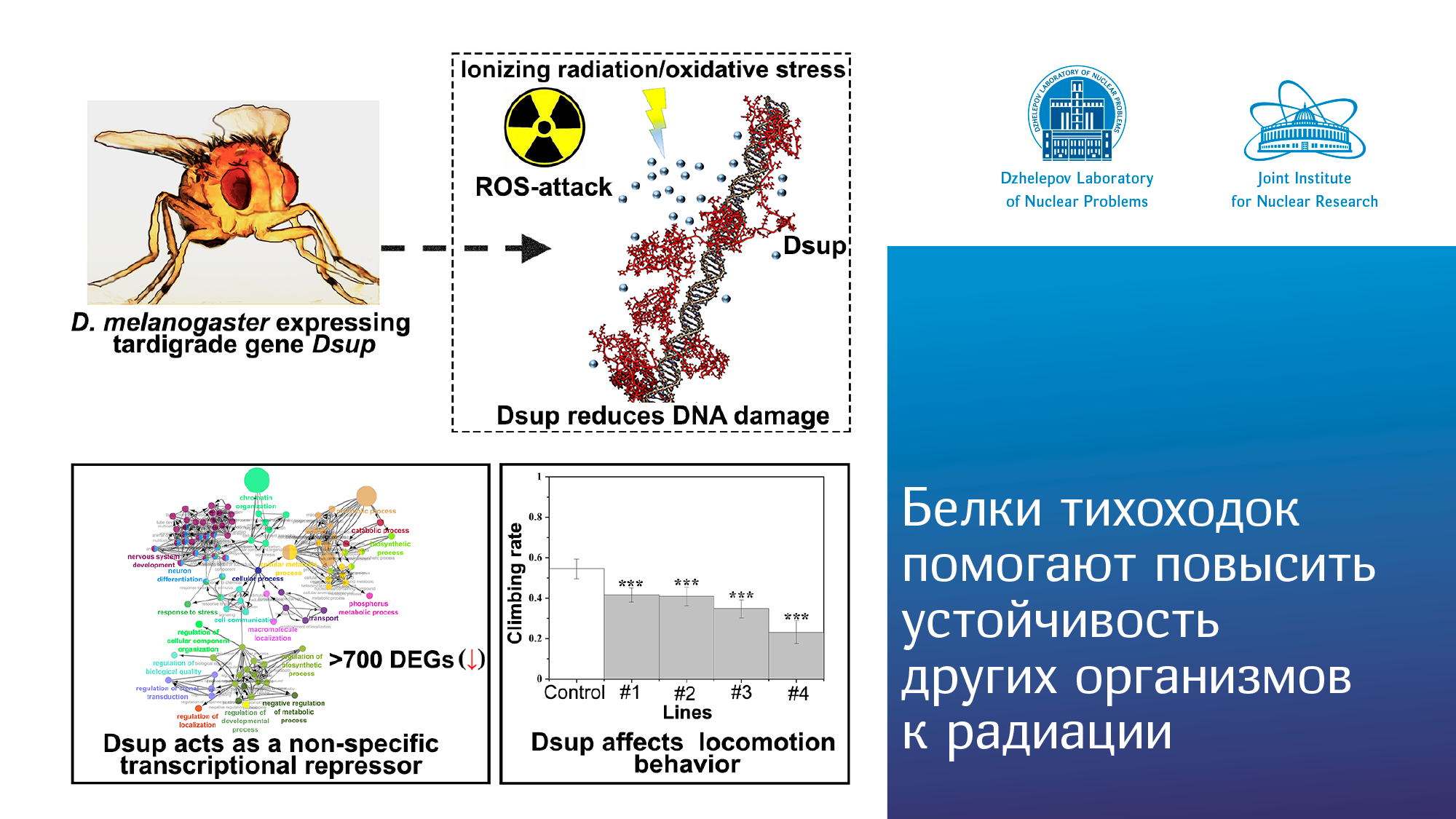
12.04.2024
Новости лаборатории
Сегодня исполняется 111 лет со дня рождения первого директора ЛЯП ОИЯИ Венедикта Петровича Джелепова.
11.04.2024
Сегодня Юрий Андреевич Усов, начальник Сектора низких температур ЛЯП ОИЯИ, отмечает свой 75-летний юбилей.
09.04.2024
В прошедшую пятницу, 5 апреля 2024 г., закончила работу Научная сессия Секции ядерной физики Отделения физических наук РАН, посвященная 300-летию Российской академии наук.
09.04.2024
Видеоролик для научно-просветительского разговора «Байкал – перекресток Вселенских дорог», который прошел в рамках фестиваля «Первозданная Россия» 29 марта 2024 года в Новой Третьяковке на Крымском Валу в Москве. Мероприятие было организовано Фондом им. В.И. Вернадского и Правительством Республики Алтай.
Новости
06.04.2024
Сегодня последний день дневника. Завершили ледовые работы традиционной церемонией опускания веревочек в майны! Основные эмоции на лицах — выгорание и крайняя усталость. Все работы, запланированные на экспедицию, успешно выполнены!
05.04.2024
Завершили свертывание лагеря.
Из-за дождливой погоды решено церемонию опускания веревочек перенести на завтра.
04.04.2024
Сегодня на 2-м кластере, на 1-й, 2-й и 5-й гирляндах, поставили крест и буй, на кластере включили тестовый набор данных. На 8-й гирлянде 14-го кластера установили модули на щит.
03.04.2024
Сегодня на 1-й и 2-й гирляндах 2-го кластера смонтировали верхние секции, протестировали гирлянды с берега – все тесты успешные, опустили гирлянды до уровня метки креста; 5-ю гирлянду этого же кластера разобрали до МГ (модуля гирлянды), отвезли МГ на берег, отремонтировали и вернули к месту монтажа через пару часов, после чего приступили к монтажу верхней секции. Монтаж ведется ночью.
02.04.2024
Сегодня начали потихоньку убирать ледовый лагерь. Собрали со льда у 1-го кластера все катушки сухопутных и бракованных кабелей, шесть тестовых перемычек выгрузили в зелёный кунг на поляне, убрали пять бракованных кабелей. Собрали в лагере отдельно стоящие ящики с ОМ (10 штук) и передали их для монтажа на гирлянду, на которой 40 ОМ будут оставлены под водой до следующего года.
01.04.2024
В экспедиции не бывает 1-го апреля по давней традиции.
Продолжились работы на втором кластере: расчистили майны гирлянд 1, 2, 5. Майны сильно заросли, пришлось использовать большую бензопилу. Кроме того, их засыпало льдом и снегом. На 1-й гирлянде этого кластера сняли буй, на 2-й – дошли до верхней секции и сняли акустический модем.
01.04.2024
В прошедшую пятницу, 29 марта 2024 г., в Новой Третьяковке на Крымском Валу в Москве, на площадке фестиваля «Первозданная Россия», прошел научно-просветительский разговор «Байкал – перекресток Вселенских дорог».
31.03.2024
Сегодня продолжили работы на 13-м кластере: 9-ю гирлянду собрали до верхнего ЦМ (центрального модуля), погрузили его на 80 м для продавливания разъемов, калибровали лазер между второй и третьей секцией; на 7-й гирлянде смонтировали третью секцию, МГ (модуль гирлянды) и накладной кабель до метки зажима креста, все тесты прошли успешно.